This web page was produced as an assignment for Genetics 677, an undergraduate course at UW-Madison.
Gene Sequence and Homology
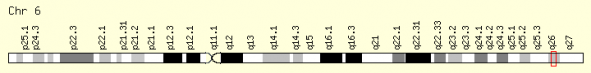
The human PARK2 gene (accession number: NC_000006.11) is on the 6th chromosome in humans and localizes to the region 6q25.2-q27 (Figure 1). In mice, the gene is on the 17th chromosome in humans and localizes to the region 17 5.91 cM (Figure 2).
Since the gene encoding the parkin protein contains over 1,000,000 base pairs, it was necessary to use the mRNA form of the gene when analyzing sequences (see sequences below). Homologs of the parkin gene exist in a diverse number of organisms such as chimpanzees, mice, chickens, c. elegans, and others. The sequence length of the gene varies between organisms, with the human variant (GI: 169790968) having the largest sequence and the dog variant containing the smallest sequence. Using the online Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST), the similarity in sequences between the human parkin gene and orthologs in other species were analyzed (1). The results are as follows:
Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) Canis lupus familiaris (Dog)
Gene name: PARK2 Gene name: PARK2
E value: 0.0 E value: 1 e -168
Bos taurus (Cow) Mus musculus (Mouse)
Gene name: PARK2 Gene name: PARK2
E value: 0.0 E value: 0.0
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) Gallus gallus (Red jungle fowl)
Gene name: PARK2 Gene name: PARK2
E value: 0.0 E value: 2 e -48
Danio rerio (Zebrafish) Drosophila melanogatser (Fruitfly)
Gene name: PARK2 Gene name: park
E value: no significant similarity E value: no significant similarity
Anopheles gambiae (Mosquito) Caenorhabditis elegans (Roundworm)
Gene name: AgaP_AGAP006580 Gene name: pdr-1
E value: no significant similarity E value: no significant similarity
Analysis
Based upon these results, orthologs of PARK2 in vertebrates have higher alignments (as determined by a lower E value) with the human PARK2 DNA sequence than do the invertebrate species. This suggests that PARK2 could have similar functions in all organisms with a central nervous system. In terms of applicability, the mouse and rat homologs would serve as good model organisms to study PARK2 and its mutant phenotypes.
Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) Canis lupus familiaris (Dog)
Gene name: PARK2 Gene name: PARK2
E value: 0.0 E value: 1 e -168
Bos taurus (Cow) Mus musculus (Mouse)
Gene name: PARK2 Gene name: PARK2
E value: 0.0 E value: 0.0
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) Gallus gallus (Red jungle fowl)
Gene name: PARK2 Gene name: PARK2
E value: 0.0 E value: 2 e -48
Danio rerio (Zebrafish) Drosophila melanogatser (Fruitfly)
Gene name: PARK2 Gene name: park
E value: no significant similarity E value: no significant similarity
Anopheles gambiae (Mosquito) Caenorhabditis elegans (Roundworm)
Gene name: AgaP_AGAP006580 Gene name: pdr-1
E value: no significant similarity E value: no significant similarity
Analysis
Based upon these results, orthologs of PARK2 in vertebrates have higher alignments (as determined by a lower E value) with the human PARK2 DNA sequence than do the invertebrate species. This suggests that PARK2 could have similar functions in all organisms with a central nervous system. In terms of applicability, the mouse and rat homologs would serve as good model organisms to study PARK2 and its mutant phenotypes.
| parkin_gene_sequences.doc |