This web page was produced as an assignment for Genetics 677, an undergraduate course at UW-Madison.
Protein Interactions
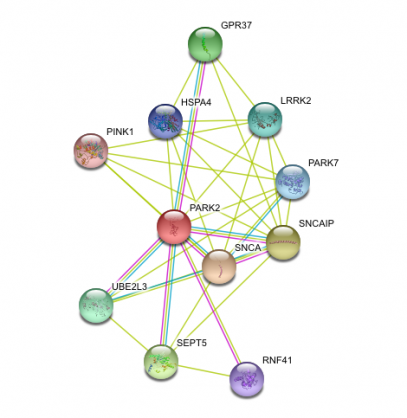
The Search Tool for the Retreival of Interacting Genes/Proteins (STRING) is an online database that shows direct and indirect protein-protein interactions. Using the STRING search, the following protein interactions were shown to be associated with parkin (Figure 1). This protein network pertains to Homo sapiens; however, protein networks for other species homologs of pzrkin were also given in the search results. Two proteins of note in the parkin network are PINK1 and alpha-synuclein (shown as SNCA). PINK1 is localized in the mitochondria and has been shown to recruit parkin to the mitochondria in a stress-dependent response (2). Once in the mitochondria, parkin is thought to induce autophagic degradation of the damaged organelle. Alpha-synuclein is a protein that is involved in the regulation of dopamine transport and release from neuron cells. Alpha-synuclein is a soluble protein, and can form the filamentous aggregates known as lewy bodies, which are the major non-amyloid intracellular inclusions found in neuron cells of patients with PD.
References
1. STRING. http://string.embl.de/
2. Matsuda, N., Sato, S., Shiba, K., Okatsu, K., Saisho, K., Gautier, C. A., Sou, Y. S., Saiki, S., Kawajiri, S., Sato, F., Kimura, M., Komatsu, M., Hattori, N., Tanaka, K. (2010). PINK1 stabilized by mitochondrial depolarization recruits Parkin to damaged mitochondria and activates latent Parkin for mitophagy. J Cell Biol, 189(2), 211-21. Doi: 10.1083/jcb.200910140
2. Matsuda, N., Sato, S., Shiba, K., Okatsu, K., Saisho, K., Gautier, C. A., Sou, Y. S., Saiki, S., Kawajiri, S., Sato, F., Kimura, M., Komatsu, M., Hattori, N., Tanaka, K. (2010). PINK1 stabilized by mitochondrial depolarization recruits Parkin to damaged mitochondria and activates latent Parkin for mitophagy. J Cell Biol, 189(2), 211-21. Doi: 10.1083/jcb.200910140