This web page was produced as an assignment for Genetics 677, an undergraduate course at UW-Madison.
Protein Domains
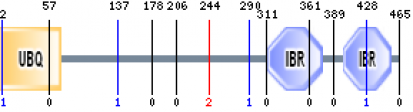
The human parkin protein (accession number: NP_004553.2) is 465 amino acids in length (click here to view sequence). Using the SMART program, three domains were found to be in the protein sequence of parkin (1):
1. A ubiquitin homolog (UBQ) ranging from 1-72 aa (E value = 2.95e-16)
2. In between ring fingers (IBR) ranging from 313-377 aa (E value = 4.49e-14)
3. In between ring fingers (IBR) ranging from 401-457 aa (E value = 1.42e-01)
1. A ubiquitin homolog (UBQ) ranging from 1-72 aa (E value = 2.95e-16)
2. In between ring fingers (IBR) ranging from 313-377 aa (E value = 4.49e-14)
3. In between ring fingers (IBR) ranging from 401-457 aa (E value = 1.42e-01)
The UBQ domain is involved in the regulated turnover of proteins required for controlling cell cycle progression. The ubiquitin-like domain is thought to bind the PSMD4 subunit of 26S proteasomes (2). A naturally occurring Arginine 42-Proline mutation in theUBQ domain impairs this proteasome binding and is thought to contribute to autosomal recessive juvenile PD (3). The IBR domains are usually located in between pairs of zinc RING fingers.
There are 5 isoforms of parkin that are produced by alternate splicing. Isoform 1 is considered to be the "canonical" sequence, from which all other isoforms can be related to. Each isoform is different from the canonical sequence as follows:
-isoform 2: missing a.a. 179-206
-isoform 3: missing a.a. 1-79 and 298-465, substitution of AGCPNSL → VCLLPGM in a.a. 291-297
-isoform 4: missing a.a. 1-191
-isoform 5: substitution of V → VGTGDTVVLRGALGGFRRGV in a.a. 290, substitution of FAFCREC → YGQRRTK in a.a. 362-368, missing a.a. 369-465
There are 5 isoforms of parkin that are produced by alternate splicing. Isoform 1 is considered to be the "canonical" sequence, from which all other isoforms can be related to. Each isoform is different from the canonical sequence as follows:
-isoform 2: missing a.a. 179-206
-isoform 3: missing a.a. 1-79 and 298-465, substitution of AGCPNSL → VCLLPGM in a.a. 291-297
-isoform 4: missing a.a. 1-191
-isoform 5: substitution of V → VGTGDTVVLRGALGGFRRGV in a.a. 290, substitution of FAFCREC → YGQRRTK in a.a. 362-368, missing a.a. 369-465
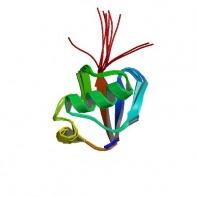
Figure 2: Structure of the parkin protein (4).
The parkin protein is post-translationally modified through auto-ubiquitinylation in an E2 dependent manner, leading to its own degradation.
Analysis
The parkin protein is thought to contain two RING finger domains that allow the protein to bind to substrates for ubiquitination. It is not clear why the SMART program did not identify these two domains in analyzing the parkin motifs. Even so, point mutations in both the UBQ and RING finger domains cause defects in parkin’s activity, subsequently leading to autosomal recessive juvenile PD.
References
1. SMART. http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/
2. Uniprot. http://www.uniprot.org/
3. PubMed. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure
4. Image of protein structure. mupfc.marshall.edu/~baker159/
2. Uniprot. http://www.uniprot.org/
3. PubMed. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure
4. Image of protein structure. mupfc.marshall.edu/~baker159/